The artificial intelligence landscape is experiencing a revolutionary shift from reactive systems to autonomous, goal-driven intelligence. Agentic AI represents this transformation—a paradigm where AI systems don’t just respond to prompts but actively think, plan, and execute complex tasks with minimal human oversight. This article answers the question “what is agentic ai”
Understanding Agentic AI
Agentic AI is an advanced form of artificial intelligence that possesses agency—the ability to act independently, make decisions, and pursue specific goals autonomously. Unlike traditional AI systems that wait for commands or follow predefined rules, agentic AI can perceive its environment, formulate strategies, execute actions, and adapt to changing conditions in real-time.
At its core, agentic AI combines the generative capabilities of large language models with the precision of traditional programming, adding the crucial element of autonomous decision-making. These systems can break down complex, multi-step problems into manageable subtasks and work through them methodically, moving beyond simple query-response patterns toward structured problem-solving approaches.
How Agentic AI Differs from Traditional AI
The fundamental distinction lies in their operational philosophy and capabilities:
Traditional AI Systems
- Reactive: Wait for user input and respond accordingly
- Rule-based: Follow predetermined algorithms and fixed logic
- Task-specific: Designed for particular functions without deviation
- Human-dependent: Require constant oversight and specific instructions
Agentic AI Systems
- Proactive: Anticipate needs and take initiative to address potential issues
- Adaptive: Learn from environment and adjust strategies dynamically
- Goal-oriented: Work toward broader objectives with autonomous planning
- Context-aware: Understand situations and make informed decisions independently
According to research, agentic AI systems demonstrate higher levels of autonomy compared to traditional AI agents, with the ability to make independent decisions without constant human oversight. They focus on achieving long-term goals rather than executing isolated tasks, adapting their strategies as necessary to accomplish these objectives.
Core Characteristics of Agentic AI
Autonomy and Independence
Agentic systems operate with minimal human intervention, capable of making decisions and executing tasks independently. They can navigate complex, unpredictable environments while maintaining progress toward their core objectives.
Reasoning and Planning
These systems employ sophisticated cognitive modules that assess situations, recall past experiences, generate strategic options, and decide on optimal actions aligned with their goals. They can evaluate multiple scenarios and consider outcomes like cost, speed, and impact to identify the most effective course of action.
Adaptability and Learning
Agentic AI continuously improves through experience, using feedback loops for optimization. After executing actions, agents observe and evaluate results, comparing them against expectations and updating their internal models for future decision-making.
Multi-step Execution
Unlike simple automation tools, agentic systems can handle complex workflows that require sequential decision-making, error handling, and dynamic adjustment of approaches when encountering obstacles.
How Agentic AI Works
The architecture of agentic AI operates through a continuous closed-loop system consisting of five key components:
1. Perception Module
Acts as the agent’s sensory system, gathering and interpreting diverse data from structured databases, unstructured text, sensor data, and visual images. Using technologies like computer vision and natural language processing, it filters noise and delivers contextual environmental snapshots.
2. Cognitive Layer
The reasoning brain that processes information and makes decisions. It leverages AI models such as inference engines, neural networks, or large language models to assess situations, generate strategic options, and choose optimal actions based on predefined goals.
3. Planning Component
Formulates strategic plans aligned with objectives by evaluating different scenarios and considering various outcomes. For instance, a supply chain agent encountering delays will proactively explore alternative routes and logistics to minimize disruption.
4. Action Module
Executes decisions through integration with APIs, robotic automation, or direct physical actuators. Whether updating databases, triggering business processes, or controlling equipment, this module ensures decisions translate into concrete outcomes.
5. Learning System
Continuously observes and evaluates results, comparing them against expectations and updating the agent’s models. This enables progressive refinement of accuracy and effectiveness through successive cycles.
Real-World Applications and Use Cases
Business Operations
- Customer Service: Autonomous handling of inquiries, issue resolution, and personalized support across multiple channels
- Supply Chain Management: Optimizing logistics, predicting disruptions, and automatically adjusting supplier selection based on real-time conditions
- Financial Services: Risk assessment, fraud detection, and automated investment recommendations based on market analysis
Healthcare and Life Sciences
- Diagnostic Assistance: Gathering patient data and suggesting potential diagnoses based on medical history and symptoms
- Treatment Planning: Creating personalized care plans and optimizing therapeutic approaches
- Administrative Automation: Streamlining billing, scheduling, and insurance processes
Technology and Development
- Software Development: Automated code generation, debugging, testing, and documentation creation
- IT Support: Proactive system monitoring, issue identification, and resolution before problems escalate
- Cybersecurity: Real-time threat detection, adaptive threat hunting, and automated response to security incidents
Benefits and Advantages
Enhanced Productivity
Agentic AI can automate both routine and complex tasks, freeing human workers to focus on higher-value activities that require creativity and strategic thinking. Companies implementing these systems have reported up to 90% reduction in operational costs for routine tasks.
Improved Decision-Making
These systems can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and make informed decisions faster than human operators. They utilize machine learning to filter and analyze data, learning from experience to continuously improve decision-making processes.
24/7 Operations
Unlike human workers, agentic systems can operate continuously without breaks, significantly increasing operational efficiency and responsiveness. They can handle multiple tasks simultaneously across various domains.
Scalability and Flexibility
Agentic AI can scale horizontally without proportional increases in staffing, allowing organizations to support more business use cases without linear headcount growth. They adapt to changing circumstances and requirements with real-time responsiveness.
Challenges and Limitations
Trust and Explainability
One of the primary challenges is ensuring these autonomous systems can justify their actions and decisions. Without transparency, organizations struggle to trust autonomous processes. Essential capabilities include comprehensive action logging and decision pathway visibility.
Safety and Control
Agentic systems require well-defined operational boundaries, including role-based access controls, approval workflows for high-impact changes, and sandboxed environments for testing.
Technical Complexity
These systems present unique debugging challenges compared to deterministic systems, requiring specialized observability tools and versioning systems. Current frameworks still have limitations in memory retention, multi-agent coordination, and tool integration.
Organizational Change
Deploying agentic AI isn’t purely technical—it requires cultural alignment and new collaboration models between staff and AI agents. Teams must accept responsibility shifts from humans to autonomous systems.
Multi-Agent Systems and Collaboration
The evolution toward multi-agent systems represents the next frontier in agentic AI. These systems involve multiple specialized AI agents working together, each with distinct roles and capabilities, coordinating to achieve complex objectives that would be impossible for single agents.
Types of Multi-Agent Architectures
- Cooperative Systems: Agents share information and work toward common goals
- Competitive Systems: Agents pursue individual objectives while competing for resources
- Mixed Systems: Blend cooperative and competitive elements
- Hierarchical Systems: Introduce levels of authority with senior agents coordinating junior agents
Benefits of Multi-Agent Collaboration
- Specialization: Each agent can focus on specific domains of expertise
- Resilience: If one agent fails, others can redistribute tasks
- Scalability: Complex problems can be broken down into manageable pieces
- Efficiency: Parallel processing of multiple subtasks
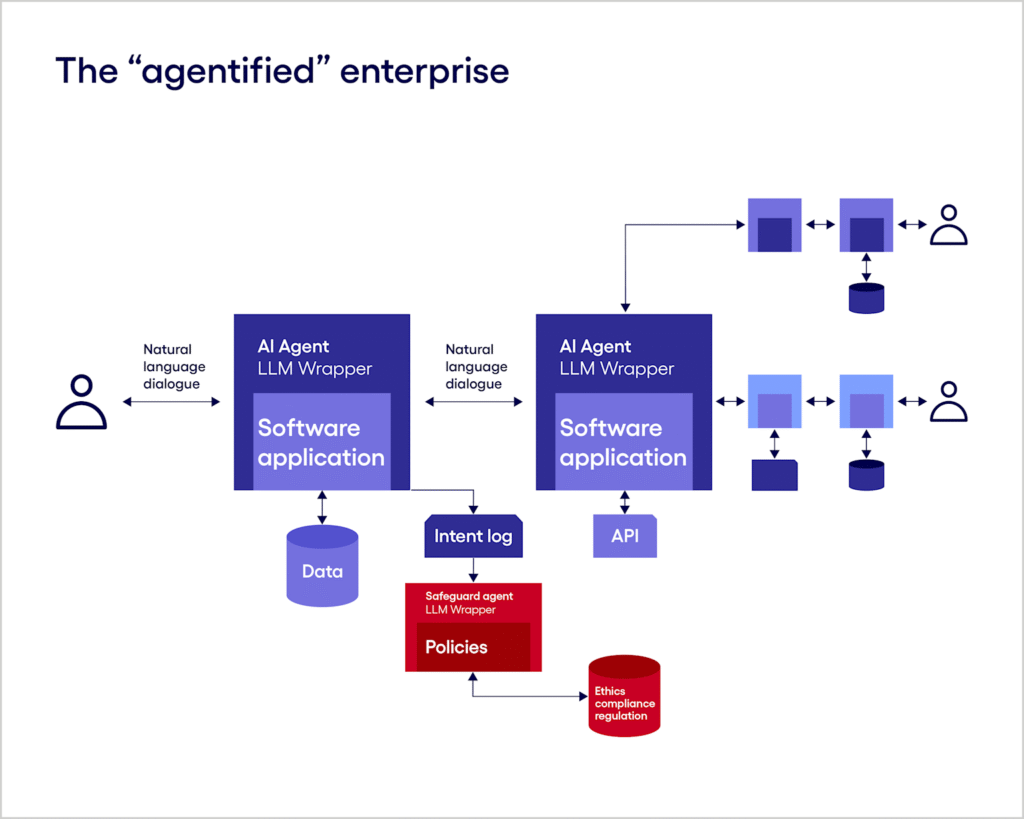
The Future of Agentic AI
Emerging Trends for 2025 and Beyond
Increased Personalization: AI agents will provide more tailored experiences based on user preferences and behavior patterns.
Enhanced Interoperability: Greater integration between different tools and platforms, enabling seamless collaboration across diverse systems.
Democratized Development: Easier-to-use frameworks making agentic AI accessible to non-specialists, accelerating adoption across industries.
Regulatory Frameworks: Development of governance structures and ethical guidelines to manage autonomous agent behavior responsibly.
Market Projections
According to industry research, the global agentic AI tools market is experiencing explosive growth, projected to reach $10.41 billion in 2025 with a compound annual growth rate of approximately 56.1%. Gartner predicts that by 2029, agentic AI will autonomously resolve 80% of common customer service issues without human intervention.
Implementation Considerations
Framework Selection
Organizations have numerous options for building agentic systems, including LangGraph, Microsoft AutoGen, CrewAI, and emerging platforms like Anaconda AI Navigator. The choice depends on specific requirements such as enterprise-grade reliability, multi-agent coordination needs, and integration complexity.
Key Success Factors
- Clear Goal Definition: Establishing well-defined objectives and success metrics
- Robust Testing: Implementing comprehensive validation and testing protocols
- Gradual Rollout: Starting with low-risk applications before expanding to critical systems
- Continuous Monitoring: Establishing observability and performance tracking mechanisms
Conclusion
Agentic AI represents a fundamental shift in how we conceive and deploy artificial intelligence systems. By moving from reactive, prompt-dependent tools to proactive, goal-oriented agents, organizations can achieve unprecedented levels of automation, efficiency, and innovation.
The technology is rapidly maturing, with increasing numbers of organizations already implementing agentic solutions across diverse industries. However, successful deployment requires careful consideration of technical, organizational, and ethical factors.
As we advance into 2025 and beyond, agentic AI will continue evolving toward more sophisticated multi-agent systems, enhanced personalization capabilities, and broader accessibility. Organizations that understand and strategically implement these technologies today will be best positioned to harness their transformative potential in the autonomous intelligence era.
The question is no longer whether agentic AI will reshape industries and workflows—it’s how quickly organizations can adapt to this new paradigm of autonomous, intelligent systems working alongside human teams to achieve previously impossible goals.
FAQs
- What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to autonomous AI systems capable of independently planning, reasoning, and executing complex tasks with minimal human input. It acts proactively to achieve goals rather than just responding to commands. - How does Agentic AI differ from traditional AI?
Traditional AI is largely reactive and rule-based, responding to specific inputs. Agentic AI is proactive, reasoning through multi-step tasks, adapting to changing contexts, and making autonomous decisions aligned with larger objectives. - What are the core components of an Agentic AI system?
Key components include perception (gathering data), reasoning (analyzing and making decisions), planning (formulating actions), execution (carrying out tasks), memory (retaining knowledge), and learning (improving through feedback). - What are some real-world applications of Agentic AI?
Applications range across industries, including autonomous customer service, supply chain management, healthcare diagnostics and treatment planning, software development automation, and cybersecurity threat detection. - Is Agentic AI safe for enterprise use?
Yes, with proper guardrails such as role-based permissions, audit trails, and human oversight, Agentic AI can safely execute complex workflows while ensuring compliance and accountability. - Can Agentic AI collaborate with humans?
Agentic AI works alongside human teams by automating routine or low-value tasks, providing real-time guidance, and coordinating workflows, enhancing overall productivity without displacing human judgement. - How does Agentic AI improve over time?
Agentic AI systems continuously learn from new data and experiences via feedback loops, updating memory and refining decision-making capabilities for better outcomes and adaptability. - What industries benefit most from Agentic AI?
Industries with high-volume and complex workflows such as finance, healthcare, retail, and telecommunications derive substantial benefits from Agentic AI automation. - How is Agentic AI different from Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
RPA follows rigid, rule-based instructions, while Agentic AI autonomously makes contextual decisions, adapts dynamically, and learns from outcomes to optimize performance. - Can Agentic AI manage multi-step tasks across different tools?
Absolutely. Agentic AI coordinates actions across multiple software tools, systems, and data sources in sequence, adjusting tasks dynamically to meet goals without continuous human input.